Summary:
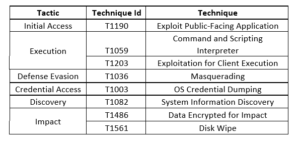
Over 3,000 internet-exposed Apache ActiveMQ servers are at risk due to critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, specifically CVE-2023-46604, with a severity score of 10.0 (CVSS v3). Apache ActiveMQ, a scalable open-source message broker, facilitates communication between clients and servers using various protocols. The vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary shell commands by exploiting serialized class types in the OpenWire protocol.
The HelloKitty ransomware operation is actively exploiting this flaw to compromise networks and encrypt devices. Researchers disclosed that at least two distinct instances have been observed where threat actors exploited CVE-2023-46604 to deploy HelloKitty ransomware binaries, aiming to extort targeted organizations. HelloKitty, an infamous ransomware operation, had its source code leaked on a Russian-speaking cybercrime forum, making it accessible to a wider range of malicious actors. The attacks commenced on October 27, just two days after Apache released the security bulletin and fixes. This indicates a case of n-day exploitation, highlighting the rapidity with which attackers move to capitalize on known vulnerabilities. The modus operandi involves the use of MSI files disguised as PNG images, obtained from a suspicious domain. These MSI files contain a .NET executable that loads a base64-encoded .NET DLL named EncDLL.
EncDLL, once executed, performs various malicious activities, including seeking and terminating specific processes, encrypting files using the RSACryptoServiceProvider function, and appending a ".locked" extension to the encrypted files. Several artifacts left behind by these attacks include unusual instances of Java.exe running with an Apache application as the parent process, loading of remote binaries named M2.png and M4.png via MSIExec, repeated but unsuccessful attempts to encrypt files log entries in activemq.log warning about transport connections failing due to an aborted connection and the presence of files or network communications associated with the HelloKitty ransomware, identifiable by specific domains and file hashes.
The exploitation of CVE-2023-46604 underscores the urgency for organizations to promptly apply security patches and highlights the swift adaptation of threat actors to leverage newly disclosed vulnerabilities for malicious activities.
Recommendations:
Threat Profile:
References:
The following reports contain further technical details: