Summary:
SysAid, an on-premise software widely used for IT service management, recently discovered a critical vulnerability in its system that could potentially compromise the security of its users. The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-47246, was a zero-day path traversal exploit allowing unauthorized code execution.The investigation revealed that a threat actor group known as DEV-0950 (Lace Tempest) had exploited this vulnerability.
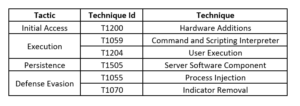
The attackers, using the alias DEV-0950 (Lace Tempest), exploited a path traversal vulnerability in the SysAid on-premises software. The attackers uploaded a WebShell and other payloads into the webroot directory of the SysAid Tomcat web service, gaining unauthorized access and control over the affected system. The PowerShell scripts were then employed to execute a malware loader named user.exe, which, in turn, loaded the GraceWire trojan into critical system processes. The attackers also utilized a second PowerShell script to erase any evidence of their actions from both the disk and the SysAid on-prem server web logs.
The attackers' techniques included deploying a CobaltStrike agent and employing various PowerShell scripts for malicious activities, such as launching a malware loader and erasing evidence from victim servers. The post-compromise cleanup involved removing the deployed payloads and associated files.
SysAid responded promptly to the discovery of the CVE-2023-47246 vulnerability, collaborating with cybersecurity experts to investigate and address the issue. The attackers, identified as DEV-0950 (Lace Tempest), exploited this zero-day vulnerability to deploy a WebShell, execute a malware loader, and load the GraceWire trojan into critical system processes. This researcher underscores the ongoing challenges in cybersecurity and the critical importance of proactive measures, including timely software updates, thorough compromise assessments, and adherence to incident response protocols, to mitigate risks posed by evolving threats.
Recommendations:
Threat Profile:
References:
The following reports contain further technical details: