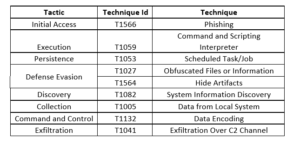
Summary:
Security researchers have identified 14 malicious npm packages designed to exfiltrate sensitive data, including Kubernetes configurations and SSH keys, from compromised systems to a remote server. These packages masqueraded as legitimate JavaScript libraries and components like ESLint plugins and TypeScript SDK tools. Upon installation, they executed obfuscated code to collect and transmit sensitive files, along with system metadata like usernames, IP addresses, and hostnames, to a domain. Threat actors continue to target open-source registries like npm, PyPI, and RubyGems with various malware, cryptojackers, and infostealers, compromising developer systems and the software supply chain.
In another recent case, an npm module called hardhat-gas-report remained benign for over eight months before receiving updates with malicious JavaScript capable of exfiltrating Ethereum private keys. This targeted approach indicates a sophisticated understanding of cryptocurrency security. Another supply chain attack involved a fraudulent npm package named gcc-patch, posing as a GCC compiler but harboring a cryptocurrency miner. Similarly, a campaign targeting PyPI leveraged a fake Python package called culturestreak to hijack system resources for cryptocurrency mining.
These attacks are not limited to a specific operating system, with campaigns increasingly targeting macOS users. The author of these malicious packages appears to be conducting a broad campaign against software developers, with the ultimate goal remaining unclear. This trend underscores the growing threat to open-source ecosystems and the importance of robust security measures and vigilance in protecting software supply chains. Developers and organizations are urged to verify package integrity and dependencies and stay informed about emerging threats in the open-source community.
Threat Profile:
References:
The following reports contain further technical details:
https://thehackernews.com/2023/09/fresh-wave-of-malicious-npm-packages.html